Are You Defining Items in QuickBooks Correctly?
[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text]
Create item records in QuickBooks carefully, and QuickBooks will return the favor by running useful, accurate reports.
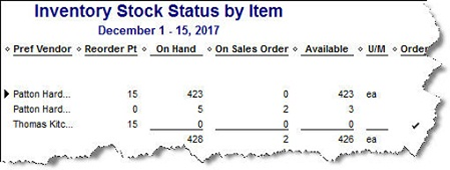
Figure 1: Clearly-defined items result in precise reports.
Obviously, you’re using QuickBooks because you buy and/or sell products and/or services. You want to know at least weekly — if not daily — what’s selling and what’s not, so you can make informed plans about your company’s future.
You get that information from the reports that you so painstakingly customize and create. But their accuracy depends in large part on how carefully you define each item. This can be a laborious process, but it’s a critical part of QuickBooks’ foundation.
QuickBooks’ Item Lineup
You may not be aware of all of your options here. So let’s take a look at what you see when you go to Lists | Item List | Item | New:
Service. Simple enough. Do you or your employees do something for clients? Training? Construction labor? Web design? This is usually tracked by the hour.
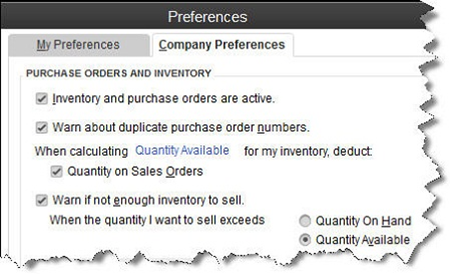
Inventory Part. If you want to maintain detailed records about inventory that contain up-to-date information about the value, quantities on hand and cost of goods sold, you must define these items as inventory parts. Before you start creating individual records, make sure that QuickBooks is set up for this purpose. Go to Edit | Preferences | Items & Inventory | Company Preferences and select the desired options there, like this:

Figure 2: QuickBooks needs to know that you’re planning to track at least some items as inventory parts.
Inventory Assembly. Just what it sounds like; it’s sometimes referred to as a Bill of Materials. Do you sell items that actually consist of multiple individual products, services and/or other charges (though you may also sell the parts separately)? If you’re planning to track the compilations as individual units, then you must define them as assemblies.
Non-Inventory Parts. If you don’t track inventory, you can set up items as non-inventory parts. Even if you do track inventory, there may be times when you’ll want to use this designation. For instance, you might sell something to a customer that they asked you to obtain, but you don’t plan to stock it. In that case, QuickBooks only records the incoming and outgoing funds.
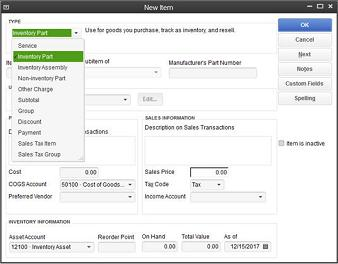
Figure 3: The New Item window looks a bit intimidating, but it’s critical that you complete it thoroughly and correctly. We can help you get started.
Other Charges. This is a catch-all category for items like delivery charges or setup fees. You can’t designate a unit or measure here; they’re just standard costs.
Groups. Unlike assemblies, these are not recorded as individual inventory units. Use this designation when you sell a combination of items together frequently but you don’t want them tracked as one entity.
Discount. This is a fixed amount or a percentage that you subtract from a subtotal or total.
Payment. Normally, you would use the Receive Payments window to record a payment made. But if your customer has made a partial or advance payment upfront, use this item to subtract it from the total when you create the invoice or statement.
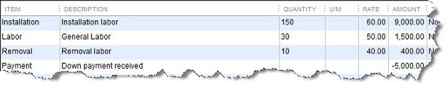
Figure 4: Use the Payment item to record an upfront remittance.
Sales Tax Item. One sales tax, one rate, one agency. Sales Tax Group. If a sale requires two or more sales tax items, QuickBooks calculates the total and displays it for the customer, but the items are tracked individually.
Additional Actions
The Item menu provides other options for working with items. You can:
- Edit or delete
- Duplicate
- Make inactive
- Find in transactions and
- Customize the list’s columns.
Let us know if you’re not confident about items you’ve already created or if you’re just getting started with this important QuickBooks feature. Some extra work and attention upfront can save you from hours of back-tracking and frustration – and from reports that don’t tell the truth.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]
6 Tips for Avoiding Digital Clutter
6 Tips for Avoiding Digital Clutter What is “Digital Clutter” and why do we need to avoid it? Although there isn’t a true definition for the phrase, we can define the term “clutter” and apply it to the digital world. “Clutter” is defined as a collection of things lying about in an untidy mess. Although…
Enduring Your Race
Enduring Your Race Every Year in Australia, an endurance race is held. It stretches from Sydney to Melbourne totaling 543.7 miles. For a world class athlete it takes five days to run. These athletes are young, professionally trained, and receive huge sponsorships Cliff Young was a very unlikely competitor in the race. At the age…
Transitioning from Employee to Entrepreneur
Transitioning from Employee to Entrepreneur If you are out of work, have you ever considered creating your own job? As of April 2013, 7.5% of the American population are unemployed. The downturn of the economy has led many to wonder where they are going to find work, but has also opened opportunities for many to…
